ReadyAI Lesson Plans
Elementary Schools
Content
Units
- Demonstration Lesson: Meet Your AI Friend
- Unit 1: Meet Your AI Friend
- Unit 2: Scaring Contest & Rebounce
- Unit 3: Peekaboo AI
- Unit 4: Speech Generation
- Unit 5: American Idol AI
- Unit 6: Object Recognition & Manipulation
- Unit 7: Tick Tock Bot
- Unit 8: Keep Away & Quick Tap
- Unit 9: Landmark-based Navigation & Cozmo’s Freetime
- Unit 10: Project Planning
- Unit 11: Project Creation
- Unit 12: Project Rehearsal
Curriculum Overview
Who Made This?
ReadyAI believes that all students should have access to artificial intelligence, not only students with computer science backgrounds or those who attend schools with highly developed technology programs.
AI is the future, and students must be prepared for it. At ReadyAI, we want to make K-12 AI education a reality and help students to be empowered to use AI to change the world.
ReadyAI is built on three basic tenets:
- We teach AI for social good. Sure, we get into some heavy material, but the core of our curriculum surrounds impacting society positively through AI, all the while recognizing the ethical concerns and the inevitable societal impact AI technology will raise.
- Learning AI is fun. W put an emphasis on the non-technical components of learning, combining art and multimedia. Students learn computer science, but they learn it in the context of their interests and power all their work with not just STEM, but STEAM education, infusing their work with what makes us human.
- Project-based Learning. Students learn through playing and building up ideas with teammates. Thus, students also learn soft-skills such as presentation techniques, leadership, and collaboration.
ReadyAI believes that AI must be broached early. That’s why we partnered with schools and afterschool programs across the U.S. and the world to develop and test this interactive curriculum.
Who is this for?
This curriculum focuses on later elementary school students, ideally Grades 4-6.
However, this curriculum is not limited to those ages. Younger students, including Grades 1-3 have already benefited from this curriculum. We might suggest exploring our early elementary age curriculum, though, if this group is your target audience.
Elementary School Teachers, After School Programs, and Homeschoolers
ReadyAI has piloted this curriculum with school systems as well as after school programs such as the Boys & Girls Club. We also have parents who want their children to follow an introductory curriculum that teaches AI concepts. Really, we encourage everyone to begin learning about AI and how to engage it in individually and socially beneficial ways. This curriculum requires no prerequisite AI skills or computer science background.
Course Structure
This curriculum overview is intended to provide the user a series of theoretical and contextual models for using an AI unit and a connected device to teach AI concepts to middle school students who have only a basic understanding of computer functionality. Unlike our middle school curriculum, this curriculum focuses on scratch based programming and differentiating between sequential and rule based coding. Additionally, this lesson is heavily gamified, allowing students to play a game, discuss how AI plays a role in it, and then try to produce a small version of the game again. Each lesson closes with discussing how the students used AI in their coding and what practical applications this technology has.
In this overview, you will find the course objectives, lesson objectives, and key activities meant to reinforce those objectives. Within the 12 lesson sequence itself, you will find assessment techniques ranging from oral discussion to multiple choice assignments. These can be used as the mode of instruction dictates.
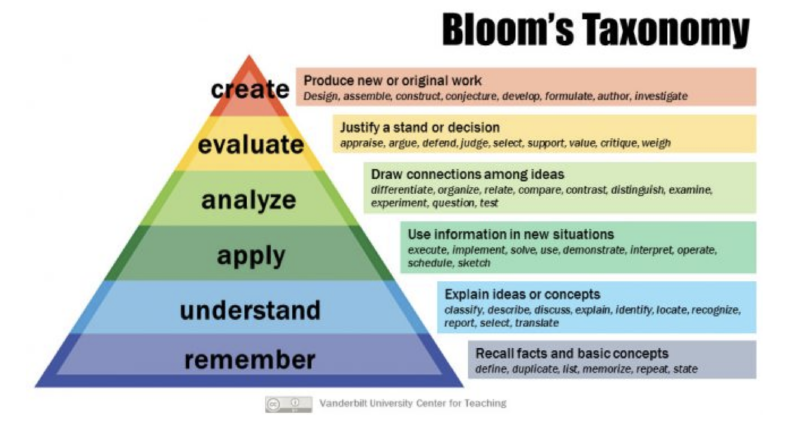
This curriculum also relies on Bloom’s Taxonomy 2.0, with “Creation” being placed as the highest level of critical thinking. In fact, the entire eight-lesson series culminates in project-based learning of AI concepts.
Technology Requirements
ReadyAI’s curriculum requires students to have AI units and connected devices, which ReadyAI can provide. Lessons also come with PowerPoints, and ReadyAI encourages teachers to use the PowerPoints to engage students. Finally, if instructors can connect their device powering the AI unit to a projector, this would greatly assist in showing some of the coding operating the AI technology. Feel free to contact info@readyai.org for additional ideas.
Getting Help
If you are a teacher or school administrator and you’d like to attend a free training on our curriculum, please contact info@readyai.org. Alternatively, we host trainings at schools as well. Please contact us about these via the same email address.
Course Objectives
Students should be able to
- define basic concepts in the field of AI;
- describe functions of AI as well as current limitations
- apply principles of coding to demonstrate understanding of AI concepts
- evaluate applications of AI technologies.
- create a project that uses AI to solve real-world problems.
AI’s Big Ideas for K-12
Big Idea #1: Computers can perceive the world using sensors.
Big Idea #2: Agents create and maintain internal representations/models of the world and use them for reasoning.
Big Idea #3: Computers can learn from data.
Big Idea #4: AI systems strive to interact comfortably with humans.
Big Idea #5: AI applications can impact society in positive and negative ways
*David Touretzky, Christina Gardner-McCune, Fred Martin, Deborah Seehorn.AI4K12.org. Envisioning AI for K-12: What should every child know about AI?
Lessons, Lesson Objectives, and Suggested Activities
| Lessons | Lesson Objectives
|
Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Lesson 1
Meet Your AI Friend |
|
Written Responses
|
| Unit 2 Scaring Contest & Rebounce |
|
Oral Responses
Written Responses
|
| Unit 3 Peekaboo AI |
|
Oral Responses
Written Responses
|
| Unit 4 Speech Generation |
|
Mini-Project
Written Responses
|
| Unit 5 American Idol AI |
|
Oral Responses
Written Responses
|
| Unit 6
Object Recognition & Manipulation |
|
Presentation
Written Responses
|
| Unit 7
Tick Tock Bot |
|
Demonstration
Written Responses
|
| Unit 8
Keep Away & Quick Tap |
|
Demonstration
Written Responses
|
| Unit 9
Landmark-based Navigation & Cozmo’s Freetime |
|
Demonstration
Written Responses
|
| Unit 10
Project Planning |
|
Demonstration
Written Responses
|
| Unit 11
Project Creation |
|
Demonstration
Written Responses
|
| Unit 12
Project Rehearsal |
|
Demonstration
Written Responses
|
Lesson Structure
Every lesson plan has a common structure that should make it easy to find what you need. Planning for a lesson starts by looking at the summary, then reviewing the agenda and teaching guide.

